Kia Optima: Troubleshooting
Kia Optima: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
|
Symptom |
Possible cause |
Remedy |
|
Hard steering |
Improper front wheel alignment Excessive turning resistance of lower arm ball joint Low tire pressure No power assist |
Correct Replace Adjust Repair and replace |
|
Poor return of steering wheel to center |
Improper front wheel alignment |
Correct |
|
Poor or rough ride |
Improper front wheel alignment Malfunctioning shock absorber Broken or worn stabilizer Broken or worn coil spring Worn lower arm bushing |
Correct Repair or replace Replace Replace Replace the lower arm assembly |
|
Abnormal tire wear |
Improper front wheel alignment Improper tire pressure Malfunctioning shock absorber |
Correct Adjust Replace |
|
Wandering |
Improper front wheel alignment Poor turning resistance of lower arm ball joint Loose or worn lower arm bushing |
Correct Repair Retighten or replace |
|
Vehicle pulls to one side |
Improper front wheel alignment Excessive turning resistance of lower arm ball joint Broken or worn coil spring Bent lower arm |
Correct Replace Replace Repair |
|
Steering wheel shimmy |
Improper front wheel alignment Poor turning resistance of lower arm ball joint Broken or worn stabilizer Worn lower arm bushing Malfunctioning shock absorber Broken or worn coil spring |
Correct Replace Replace Replace Replace Replace |
|
Bottoming |
Broken or worn coil spring Malfunctioning shock absorber |
Replace Replace |
Wheel /tire noise, vibration and harshness concerns are directly related to vehicle speed and are not generally affected by acceleration, coasting or decelerating. Also, out-of-balance wheel and tires can vibrate at more than one speed. A vibration that is affected by the engine rpm, or is eliminated by placing the transmission in Neutral is not related to the tire and wheel. As a general rule, tire and wheel vibrations felt in the steering wheel are related to the front tire and wheel assemblies. Vibrations felt in the seat or floor are related to the rear tire and wheel assemblies. This can initially isolate a concern to the front or rear.
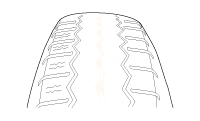
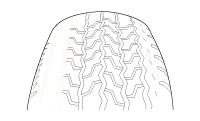
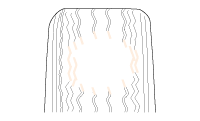
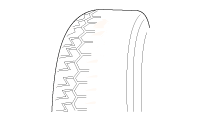
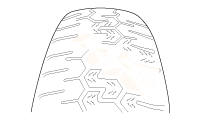
Careful attention must be paid to the tire and wheels. There are several symptoms that can be caused by damaged or worn tire and wheels. Perform a careful visual inspection of the tires and wheel assemblies. Spin the tires slowly and watch for signs of lateral or radial runout. Refer to the tire wear chart to determine the tire wear conditions and actions|
Wheel and tire diagnosis |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Rapid wear at the center |
Rapid wear at both shoulders |
Wear at one shoulder |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Partial wear |
Feathered edge |
Wear pattern |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Special Service Tools
Special Service Tools
Special Service Tools
Tool (Number and Name)
Illustration
Use
09546-26000
Strut spring compressor
Compression of coil s ...
See also:
Check Fuses
A blade type fuse test taps provided to allow checking the fuse itself without
removing if from the fuse box. The fuse is good if the test lamp lights up when
one lead is connected to the test tap ...
Replacement
1.
Loosen the wheel nuts slightly.
Raise the vehicle, and make sure it is securely supported.
2.
Remove wheel nuts, front wheel
and tire from front hub.
...
Removal
1.
Turn the ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery
negative (-) cable.
2.
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector
(A).
...