Kia Optima: Description
Kia Optima: Description
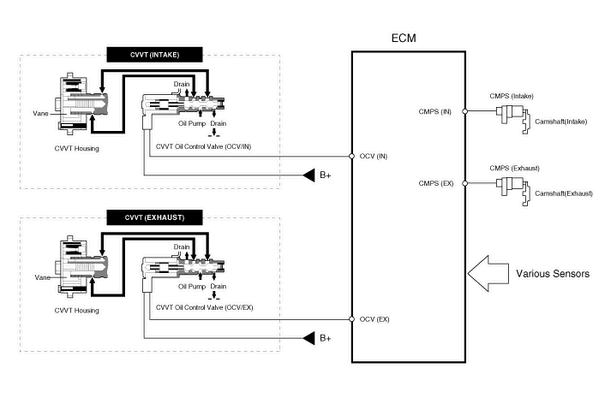
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or retards the valve timing of the intake and exhaust valve in accordance with the ECM control signal which is calculated by the engine speed and load.
By controlling CVVT, the valve over-lap or under-lap occurs, which makes better fuel economy and reduces exhaust gases (NOx, HC) and improves engine performance through reduction of pumping loss, internal EGR effect, improvement of combustion stability, improvement of volumetric efficiency, and increase of expansion work.
This system consists of| - | the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine oil to the cam phaser or runs out the engine oil from the cam phaser in accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal, |
| - | the CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil temperature, |
| - | the Cam Phaser which varies the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the engine oil. |
 Operation Principle
Operation Principle
The CVVT has the mechanism rotating the rotor vane with hydraulic
force generated by the engine oil supplied to the advance or retard chamber
in accordance with the CVVT oil control valve contro ...
See also:
Multimedia jack. Description and Operation
Description
The multimedia jack on the console upper cover is for customers who like to listen
to external portable music players like the MP3, iPod and etc., through the vehicle's
sound syst ...
Inspection
1.
Measure the output voltage between
the terminal of the wheel speed sensor and the body ground.
...
Cylinder Head. Components and Components Location
1. Camshaft bearing cap
2. Camshaft front bearing cap
3. Exhaust camshaft
4. Intake camshaft
5. Exhaust CVVT assembly
6. Intake CVVT assembly
7. Exhaus ...